 A method for homogeneous catalytic ethanol transesterification of vegetable oils (completely bio-renewable and produced in Ukraine) has been proposed, and an original technology for obtaining fatty acid ethyl esters has been developed, which can be used as an alternative biofuel for diesel engines (biodiesel fuel). The advantage of this technology over the classic one is the replacement of highly toxic methyl alcohol, obtained from natural gas, with environmentally safe bioethanol, which makes the raw material base of this process completely biologically renewable, and the synthesized ethanol biodiesel fuel more environmentally safe.
A method for homogeneous catalytic ethanol transesterification of vegetable oils (completely bio-renewable and produced in Ukraine) has been proposed, and an original technology for obtaining fatty acid ethyl esters has been developed, which can be used as an alternative biofuel for diesel engines (biodiesel fuel). The advantage of this technology over the classic one is the replacement of highly toxic methyl alcohol, obtained from natural gas, with environmentally safe bioethanol, which makes the raw material base of this process completely biologically renewable, and the synthesized ethanol biodiesel fuel more environmentally safe.
Biodiesel fuel synthesized using the technology developed at the enlarged experimental plant of the IBONH NAS of Ukraine has shown unique energy and environmental characteristics: in mixtures with petroleum-based diesel fuel in concentrations of 20-80%, the synthesized product outperforms high-quality (Euro) grade C type II diesel fuel by slightly (up to 1%) higher maximum engine power values, 2-7% higher maximum torque values, 1-3% higher engine efficiency, characterized by 1-5% lower carbon dioxide emissions, 1.3-1.5 times lower nitrogen oxide emissions, and 1.2-1.3 times lower carbon monoxide emissions, 1.9-3.3 times lower emissions of incomplete combustion products, and 1.1-2 times lower smoke opacity, with the latter four characteristics applying to the entire concentration range, including pure biodiesel fuel.
The synthesized product surpasses methanol-based fuel in terms of engine performance and environmental characteristics and is the only biodiesel fuel known today that does not increase nitrogen oxide emissions in internal combustion engines. On the contrary, it significantly reduces them, making it completely environmentally acceptable.
Currently, there are no analogues of biodiesel fuel from ethanol transesterification of oils, nor is there any technology for its production in Ukraine.
Head of development: Lyubov Kazymirivna Patryliak, Doctor of Chemical Sciences, tel. (044) 559-71-60.
The Institute has developed effective environmentally safe plant growth regulators (Ivin, Poteitin, Emistim-S, Agrostimulin, Betastimulin, Zeastimulin, Charkor, Treptol), which increase the yield of major crops by 15-20%; improve the quality of plant products; increase plant resistance to diseases, pests, and stress factors; when used in combination with pesticides, they allow a 25-30% reduction in pesticide doses, thereby reducing the pesticide load on the soil; are low-cost preparations (10-15 ml for treating 1 ton of seeds, or 5-10 ml for spraying 1 hectare of crops); ensure high profitability (1 hryvnia spent on plant growth regulators can yield an additional 15-20 hryvnia in production). The V.P. Kukhar Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry and Petrochemistry of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine has developed and registered Technical Conditions of Ukraine for the use of these plant growth regulators in the cultivation of major agricultural crops in Ukraine, according to which the limited liability company “Vysokyi Urozhay” and the State Enterprise “Interdepartmental Scientific and Technological Center ”Agrobiotech" manufacture and sell plant growth regulators on the basis of licenses provided by the Institute.

It is used in the cultivation of cereals, legumes, industrial crops, fodder crops, vegetables, fruit and berry crops, in forestry, landscape design, on flowers and lawns.
Effect on plants:
Increases germination energy and field germination of seeds, promotes root system development, increases plant resistance to diseases and stress factors, removes phytotoxic effects, has an antimutagenic effect, increases yield and quality of grown products.

Used in the cultivation of vegetable crops such as cucumbers, tomatoes, peppers, cabbage, carrots, eggplants; industrial crops such as tobacco, cotton, essential oil rose varieties; indoor plants. Particularly effective for seed treatment.
Effect on plants:
Reduces plant diseases, lowers the content of nitrates, heavy metals, and radionuclides in fruits. Provides yield increases: cucumbers – 25-70 cwt/ha; tomatoes – 35-80 cwt/ha; (in closed ground, respectively, 1.5-4.5 kg/m2 and 1.7-5.0 kg/m2); cabbage – 30-50 cwt/ha; sweet pepper – 20-40 cwt/ha. Accelerates ripening and increases early yield by 20-30%.

Used in potato cultivation technology for treating tubers and spraying plantations.
Effect on plants:
Stimulates potato growth and development in the early stages, increases disease resistance.
Hardens leaves and stems, making them more resistant to damage by Colorado beetles. Increases yield by 30-80 c/ha, increases tuber weight and starch and vitamin content.

A broad-spectrum product. It is used for seed treatment and spraying of wheat, barley, soybean, buckwheat, pea, flax, clover, alfalfa, and sorghum crops.
Effect on plants:
The product freely passes through cell membranes, activates metabolic processes, and accelerates cell division. As a result, a powerful root system and developed leaf surface quickly grow, and chlorophyll synthesis is intensified. Agrostimulin reduces the toxic effect of pesticides on crops and has an anti-mutagenic effect. It increases the yield by 10-20% and improves the quality of the grown products.

Used in the cultivation of sugar, fodder, and table beets for seed treatment and crop spraying.
Effect on plants:
Increases field germination of seeds, intensifies the development of the root system and tops, activates chlorophyll formation, increases resistance to diseases and stresses. The product actively affects the enzyme systems responsible for root growth and sugar accumulation, stimulating the flow of nutrients to the roots. Increases root crop yield by 25-60 c/ha while increasing sugar content by 0.5-1.2%.

Used in corn cultivation technologies for grain and green mass for seed treatment and crop spraying.
Effect on plants:
Reduces seed germination time, accelerates the development of young plants, enhances disease resistance, activates photosynthesis, reduces the phytotoxic effect of pesticides, and has an anti-mutagenic effect. Zeastimulin increases corn grain yield by 7-10 c/ha, green mass by 50-70 c/ha, and increases the fat and protein content in grain by 2-5%.

Rooting of green and woody plant cuttings, treatment of seedlings and saplings roots before planting in the ground, feeding the root system of trees and shrubs.
Effect on plants:
Promotes the formation of primary roots, their intensive growth and development, increases root length and accelerates root maturation. Significantly increases the profitability of vegetative propagation of plants.

Used in sunflower and rapeseed cultivation technologies for seed treatment and crop spraying
Effect on plants:
The product promotes the formation of a powerful root system and leaf surface, reduces plant disease and increases their resistance to stress factors. Increases the diameter of sunflower heads by 4-5 cm. Increases seed yield by 2.5-4.0 c/ha and oil content by 1.5-2.5%.
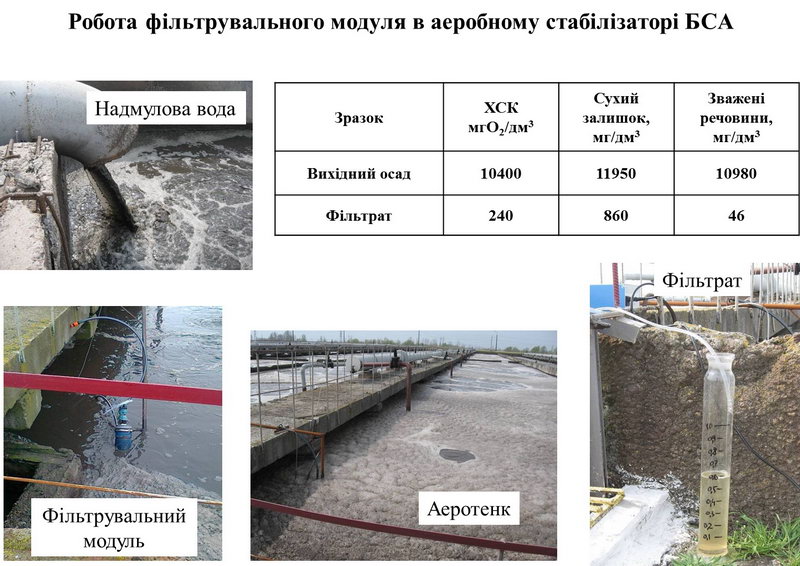
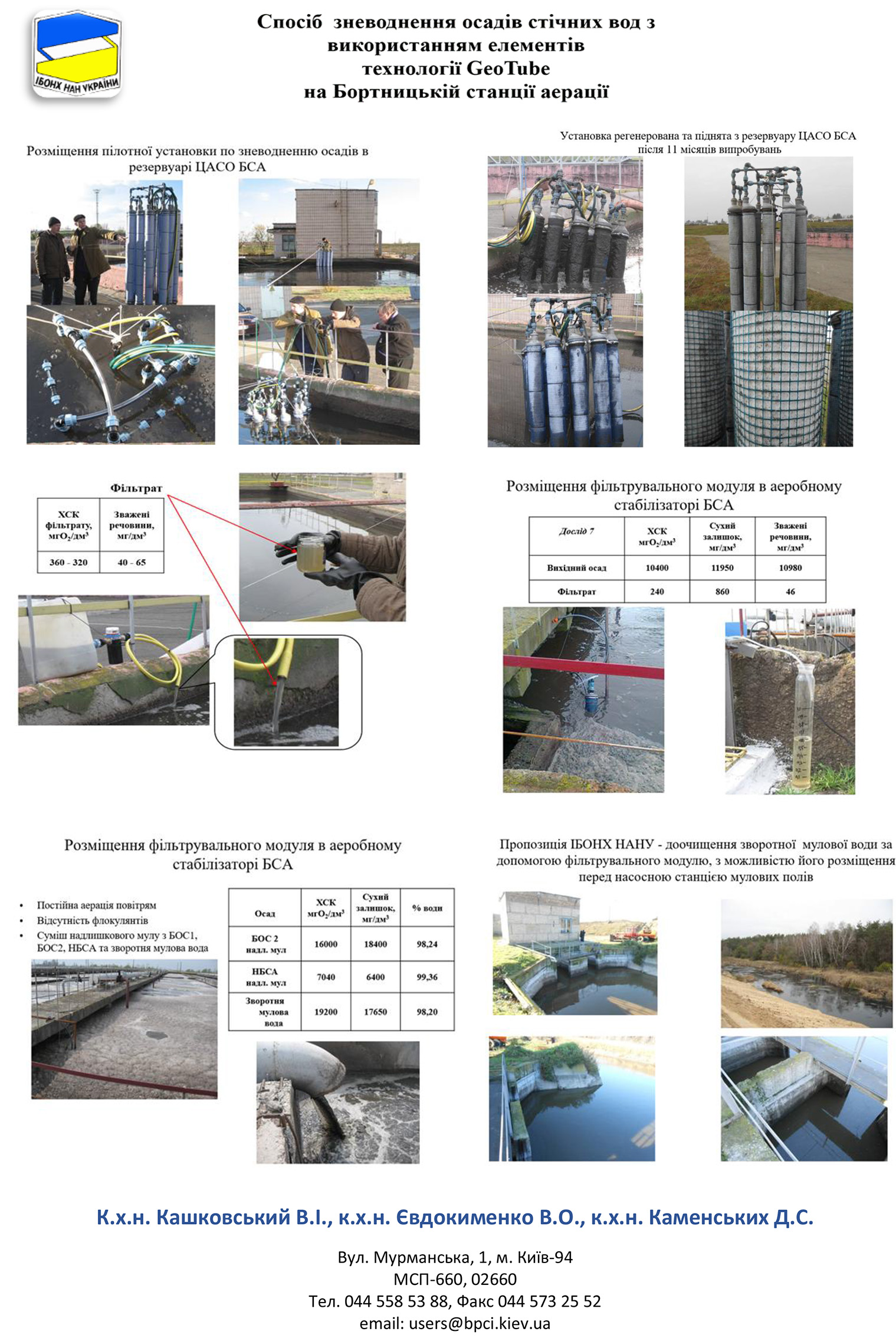
A technology for deep dewatering of wastewater sludge (using the example of the Bortnitsa aeration station BSA) using container technology (GeoTube technology elements) has been developed and the possibilities
for applying this technology in real conditions. Its high efficiency in dewatering aerobically stabilized sludge and treating return sludge water has been demonstrated. A technological scheme of processes has been developed, the implementation of which will solve an extremely acute environmental problem in Kyiv: reduce the load on sludge sites through more complete sludge dewatering and eliminate the potential threat of breach of barrier dams and catastrophic pollution of the Dnieper River; significantly improve the quality of sludge water returning from sludge sites to the “head” of the biological treatment process.


A pilot laboratory unit has been created, on which the process of dewatering sediments of various origins has been tested in the mode “sediment outside the container > water through geotextile material into the container with its constant removal.” A series of experiments on sludge dewatering was carried out at this pilot plant in the aerobically stabilized sludge (ASS) workshop of the Bortnitsa aeration station. The characteristics of the water obtained in the filtration processes are given in the tables. The regeneration modes of the filter geotextile were tested and the productivity of the pilot plant was determined.
More details on the poster:

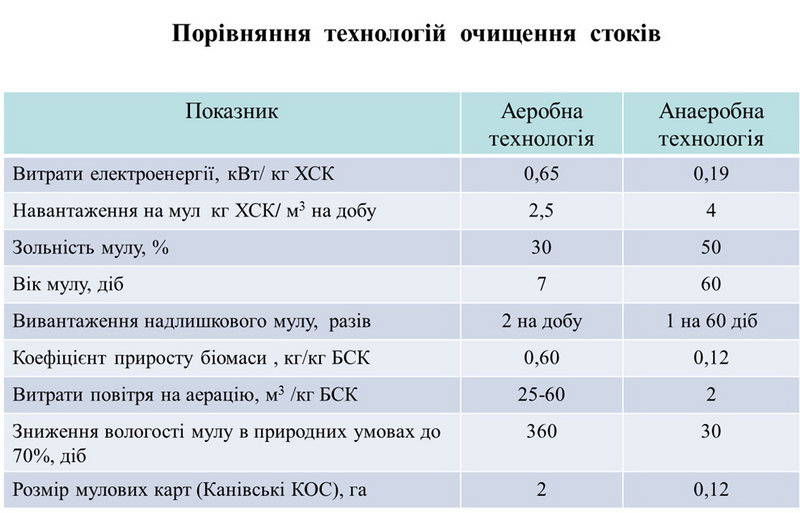
A technology has been developed for the treatment of industrial and domestic
wastewater for small towns and settlements by anaerobic digestion under psychrophilic conditions. The technology is based on the concept of modernizing existing biological treatment facilities for municipal wastewater, which involves:
Treatment of municipal wastewater in psychrophilic conditions is carried out by anaerobic microorganisms that biodegrade water-soluble organic compounds (pollutants). The use of such agrobiocenoses has made it possible to treat wastewater and reduce the amount of sludge and excess sludge by tens of times.
The implementation of this technology provides the following:
The technology has been implemented at the sewage treatment facilities in Kaniv, resulting in an increase in the depth of wastewater treatment and a reduction in the amount of sludge by approximately 50 times, which has reduced the area of sludge sites from 2.0 to 0.12 hectares.
Widespread implementation of this technology with minimal financial and resource costs can significantly improve the environmental situation in Ukraine.

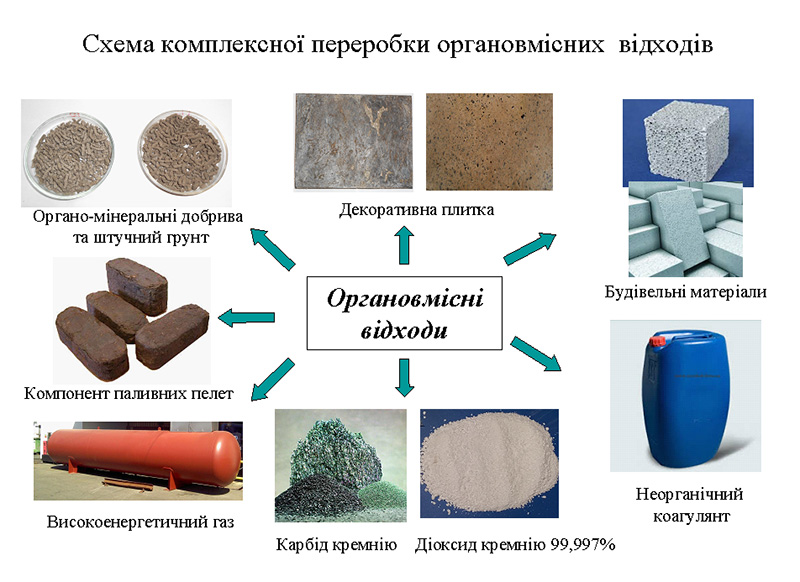
A flexible technological scheme for waste-free processing of organic waste, including municipal sewage sludge, with the production of marketable products has been developed.

Rice husks are classified as multi-tonne man-made waste. Currently, existing technologies do not provide for their comprehensive utilization. The Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry and Petrochemistry of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine has developed a waste-free method for processing rice husks into liquid products: cellulose, combustible gas with a calorific value of 3600–4000 kcal/kg, and silicon dioxide with a purity of 99.98%.
More details on the poster:
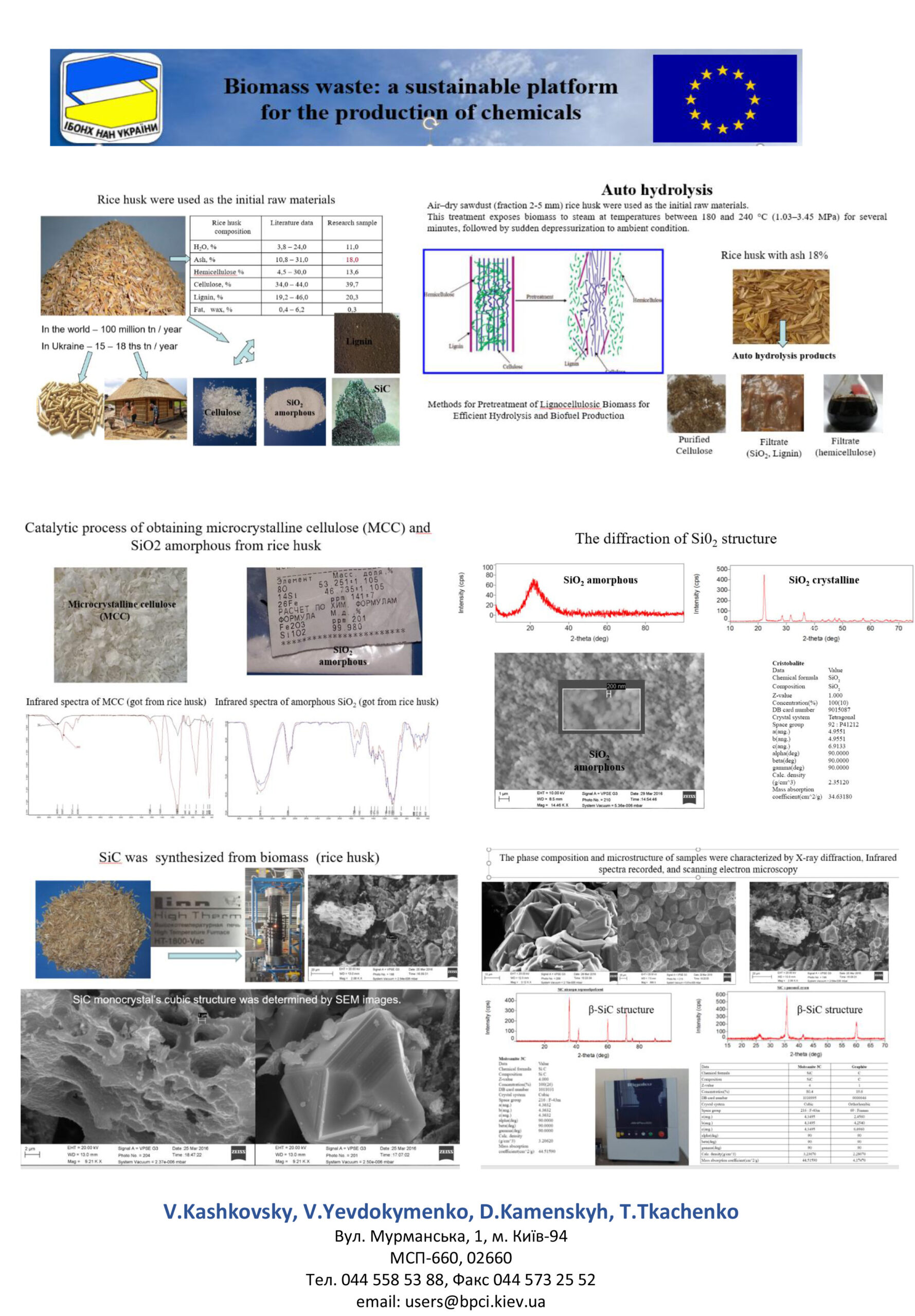
A technology has been developed for obtaining high-purity amorphous
silicon dioxide from silicon-containing waste of man-made origin, which includes the following stages: preparation of raw materials and their mixing with a fluorinating agent; heating of the mixture to a specified temperature; sublimation of the formed ammonium hexafluorosilicate; its hydrolysis in an alkaline medium; filtration and drying of silicon dioxide; regeneration of the initial fluorinating agent and ammonia solution.
Processing of the residue formed after obtaining silicon dioxide in order to extract other oxides from it or by using such residue in road construction, industrial site planning, and the creation of materials for various purposes.
The method has been tested on various silicon-containing raw materials. High-purity amorphous silica was obtained from ash from the Trypilska Thermal Power Plant, ash residues after incineration of sludge from the Bortnytska aeration station and the Kalytnyansky pig farm, as well as from quarry sand and quartz sand. All technological parameters of the process have been worked out and the necessary equipment has been selected. A technological scheme for the pilot-industrial and industrial production of amorphous silicon dioxide has been created.

Laboratory equipment has been created to study the process of explosive autohydrolysis of plant biomass in a wide range of temperatures and pressures. The research showed that all plant-based materials that went through the explosive autohydrolysis process got their structure broken down, and the mix of final products looked like a paste. Further processing of the obtained mixture allowed it to be separated into the following components: microcrystalline cellulose, hemicellulose, water-soluble sugars, and lignin. It has been established that the preliminary treatment of switchgrass under explosive autohydrolysis conditions promotes the intensification of the fermentation process (bacteria Clostridia acetobytylicum) in the direction of obtaining biobutanol, which, in our opinion, is due to the defibration of the plant material, i.e., the opening of its structure, which in turn facilitates the access of bacteria to nutrients. According to the results of the fermentation of vine millet treated under autohydrolysis conditions, the yield of butanol was 3.0 g/l. At the same time, world achievements are at the level of 2.0-2.5 g/l.
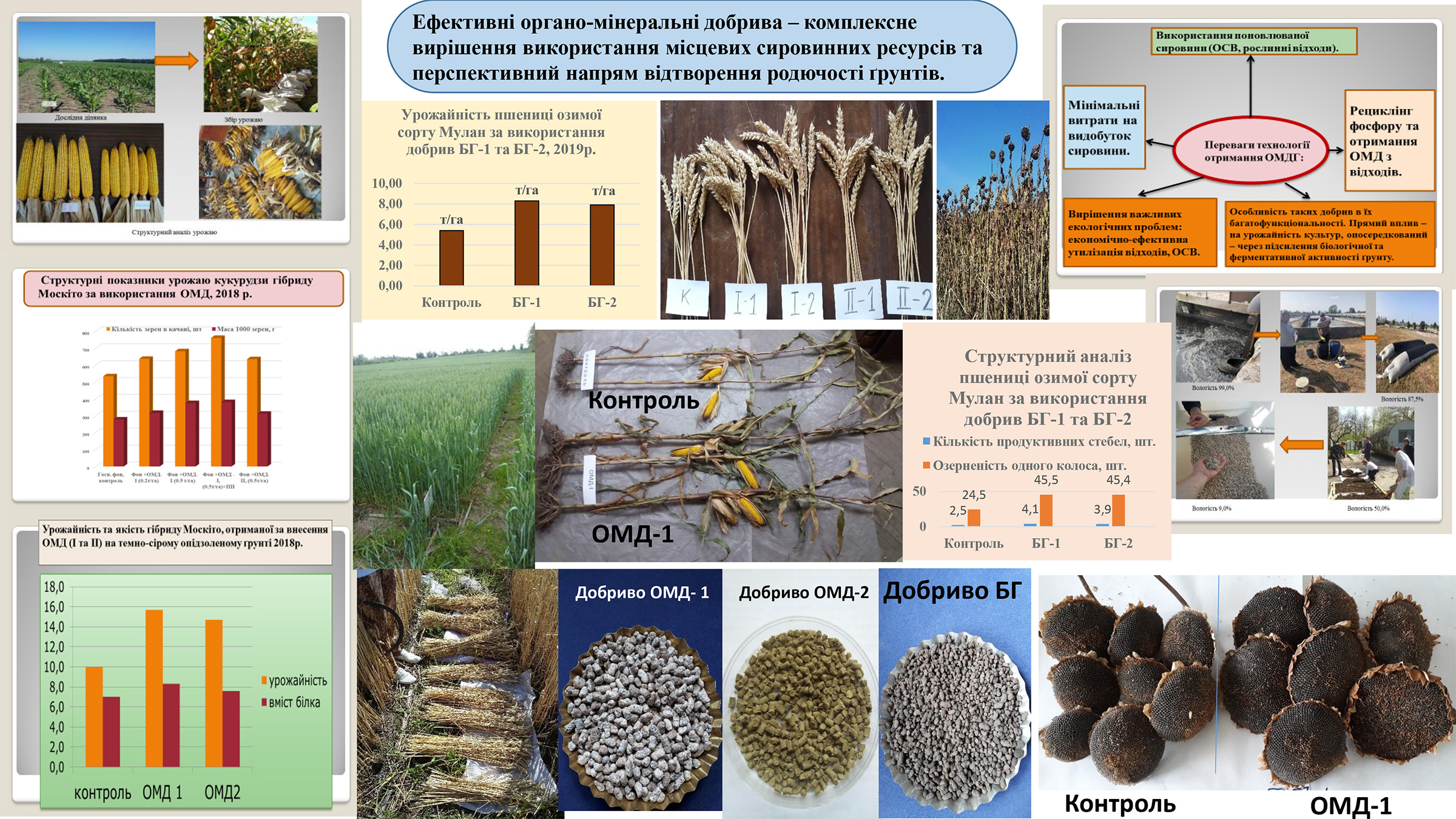
The Institute has developed a new generation of complex organo-mineral fertilizers based on sediments from the Bortnytsia aeration station and ash residues from plant waste. Field trials of these fertilizers in 2018-2019 confirmed their high agrochemical efficiency. Their use improved the nitrogen and phosphorus nutrition of the test plants, which contributed to an increase in corn yield by 5.1 tons per hectare, winter wheat by 2.9 tons per hectare, and an increase in protein content by 18.5% and 16.8%, respectively, in the absence of toxic microelements. The use of such fertilizers also contributed to improving the fertility of the experimental dark gray podzolized soil.
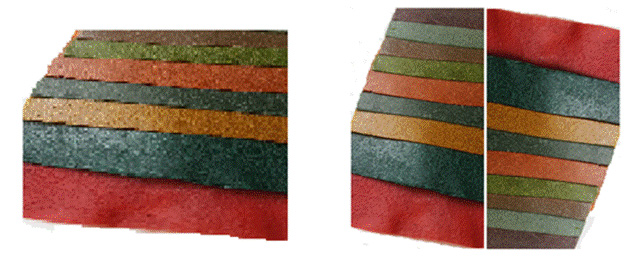
Films for use as edible packaging to protect products from mechanical damage, biological and chemical influences.
Maintain optimal moisture content and protect against staling.
The films contain nutrients: pectin, beta-carotene, vitamins B and U, betaine, fiber, sorbents. All samples are soluble in water at room temperature.
Within 10-15 minutes, the films decompose into separate particles, which then dissolve.
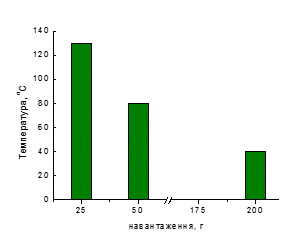
The diagram shows the dependence of the temperature at which deformation of the samples begins on a constant load. The strength limit is 10, 2.5, and 1.25 kg/cm2 at temperatures of 40, 80, and 130°C, respectively.


Specialists from the Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry and Petrochemistry of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, together with the State Scientific and Production Corporation “Kyiv Institute of Automation” and NVP “Alfa Stevia,” have developed a highly efficient technology for the comprehensive processing of leachate from landfill No. 5 of the Kyiv municipal solid waste landfill. The technological scheme is fully adapted to the existing infrastructure of landfill No. 5, designed to process up to 1,000 m3 of filtrate per day and includes the following stages:
The technology can be applied to other similar facilities. The developed technology for comprehensive treatment of filtrate has undergone sanitary and epidemiological examination at the O.M. Mazayev Institute of Hygiene and Medical Ecology of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine. The same institute approved the technical and economic feasibility study “Modernization of the technological complex for the treatment, processing, and disposal of leachate from solid waste landfill No. 5 in the village of Pidhirtsi,” which was developed based on the above-mentioned technology. As a result, a conclusion of the state sanitary and hygienic examination was received on August 14, 2008, No. 05.03.02-07/52262, according to which the specified feasibility study meets the requirements of the current sanitary legislation of Ukraine and can be used in the declared field of application (public utilities).

The process of compacting waste and the formation of a so-called filtrate containing large amounts of toxic substances as a result of the decomposition of organic compounds.
At landfill No. 5 (village of Pidhirtsi), the volume of filtrate exceeds 500,000 m3.

The accumulation of toxic filtrate and its entry into groundwater
can cause an environmental disaster.
The developed technology provides for complete purification of the filtrate, which includes stages of reagent-oxidative purification of the filtrate, its further purification by a reverse osmosis system, and discharge of water through a bioplatform into the environment, and solves the problem of concentrated sludge formed during the purification process.


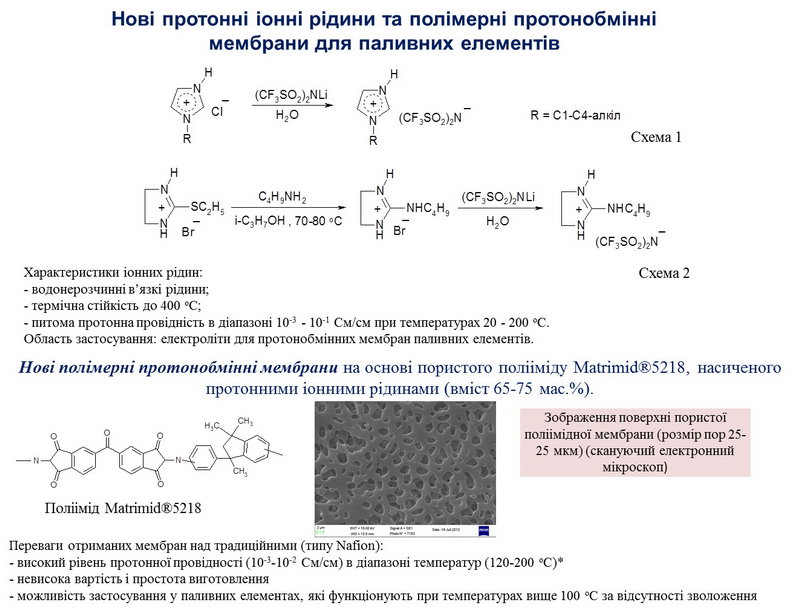
Water-insoluble protonic ionic liquids have been developed, which include cations of 1-alkylimidazolium, 2-alkylaminoimidazolinium, N-butylguanidinium, and anion bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide. It has been established that such compounds are thermally stable up to 370-400°C and have high specific ionic conductivity, reaching 10-2 cm/cm at a temperature of 180°C.
The obtained ionic liquids are promising electrolytes for use in anhydrous proton-conducting systems, in particular in polymer-electrolyte membranes for fuel cells.
Head of development: Serhii Petrovych Rohalskyi, tel.: (044) 559-46-22.
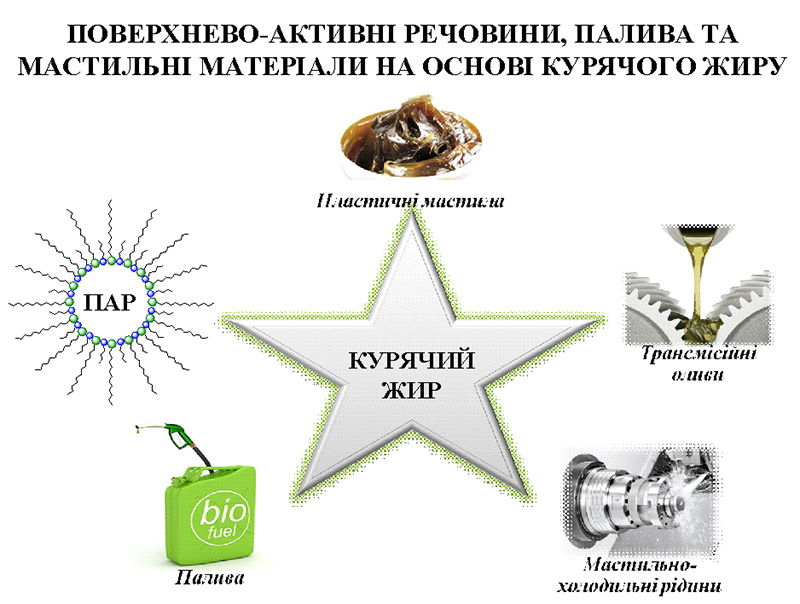
A range of functional, environmentally safe surfactants, biofuels, and lubricants have been developed based on chicken fat. Good lubricating properties provide technological fluids with high tribological characteristics, good washing and cooling properties, which allows them to be recommended not only as biofuels, but also as functional additives to technological systems for various areas with increased toxicological, hygienic, and environmental requirements. Lithium plastic grease based on chicken fat as a thickener is not inferior to commercial grease Litol-24 (GOST 21150) in terms of penetration, dropping point, mechanical stability, and other technical requirements. complex calcium grease Uniole-2M/1 (GOST 1033, TU 38.5901243), and hydrated calcium grease Solidol Grease (GOST 1033). At the same time, in terms of biodegradability, the new lubricants are 10-20% superior to existing commercial analogues, which paves the way for cheaper and more environmentally friendly production and use of lubricants.
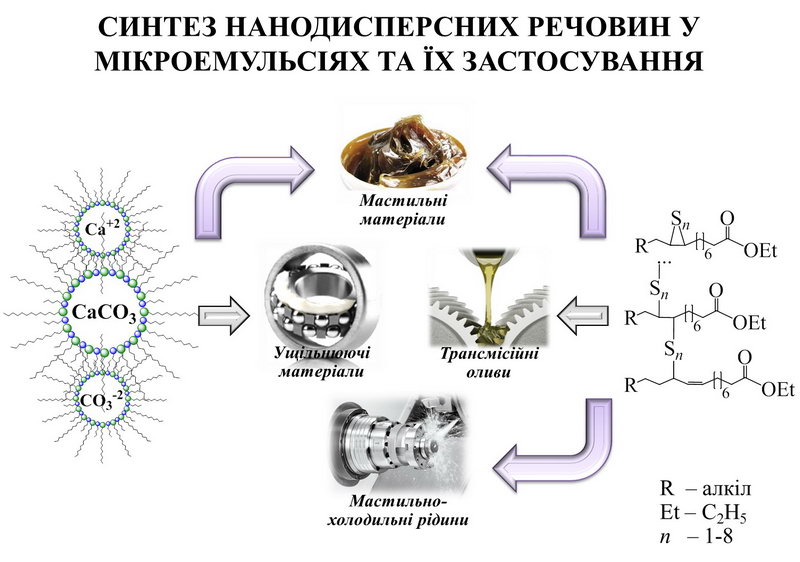
Using sulfur-containing ethyl esters of VHK oils, microemulsion-type lubricating and cooling fluids have been developed that are distinguished by their thermodynamic, sedimentation, and thermal stability, as well as transmission oils and anti-seize lubricants for rock-breaking tools, which are not inferior in terms of tribological, antioxidant and protective properties are not inferior to, and in terms of organoleptic, toxicological and environmental characteristics (biodegradability within 21 days is 93%), they significantly exceed industrial analogues. The developed oils, plastic lubricants, and lubricating and cooling fluids are comparable to the best world analogues. Their practical significance is confirmed by patents and patent applications.
Traditional lubricants are biologically difficult to decompose products (10-30%). Their production is accompanied by emissions of more than 13 tons of CO2 into the atmosphere, and during use, about 36% of them are deposited in the form of toxic oil mist on soils and roads. The Department of Surfactants of the Institute of Organic Chemistry of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine has proposed a comprehensive solution to the problem by transforming by-products from oil purification into environmentally safe multifunctional surface-active additives for lubricants.
Relevance of the problem. Today, in all economically developed countries of Western Europe, the USA, and Canada, the use of petroleum-based lubricants is prohibited by law in parks, urban and suburban recreation areas, rural, forest, and water management areas due to their high stability and slow decomposition, which causes them to remain on the surface of the ground and water bodies for a long time. Instead, environmentally friendly lubricants based on vegetable oils are widely used, which are quickly and completely absorbed by microorganisms in nature.
The IBONH of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine conducted marketing and forecast indicators for the production and use of biofuels and lubricants from renewable plant raw materials have been determined. Based on rapeseed and sunflower oils, with the addition of detergent and dispersing additives, an environmentally safe oil 10M-BIO has been developed, which, according to tests carried out at enterprises in Kyiv, meets international standards for oils for two-stroke gasoline engines.
Motor oil 10M-Bio is characterized by improved viscosity-temperature properties (according to TU U 23.2-30084964-005-2003 - kinematic viscosity at 100°C - 8.0-11.0 mm2/s (cSt); flash point – over 200°C) and meets the basic requirements of leading manufacturers of small-sized equipment such as Husquarna, Dolmar, and Stihl. It ensures high engine cleanliness, good starting qualities in cold and hot starts, perfect condition of piston rings and protection against wear and corrosion, high environmental friendliness (biodegradability according to SES-L-33-T-82 is over 95%).
Motor oil 10m-Bio is designed for use in two-stroke engines with water or air cooling by pre-mixing the oil with fuel or by separate automatic injection into the combustion chamber.
Recommended for motor scooters, mopeds, motorcycles, motor boats, chainsaws, snowmobiles, snow blowers, lawn mowers, hedge trimmers, etc.
Thanks to its high anti-corrosion properties, the oil can also be used for internal preservation of two-stroke engines during storage, transportation, and seasonal decommissioning of equipment.
10m-Bio motor oil can be mixed with various types of fuel and is recommended for use in two-stroke gasoline engines, taking into account the manufacturer's recommendations, preferably in a ratio of “oil:gasoline = 1:50.”
Thanks to the use of its own natural renewable raw materials, the cost of 10m-Bio oil is 2-4 times lower than that of similar imported oils purchased in Sweden or Germany.
10m-Bio motor oil can be supplied in 216.5-liter Euro barrels and in 5-liter and 1-liter plastic canisters. Potential manufacturer – Barva, Ivano-Frankivsk.
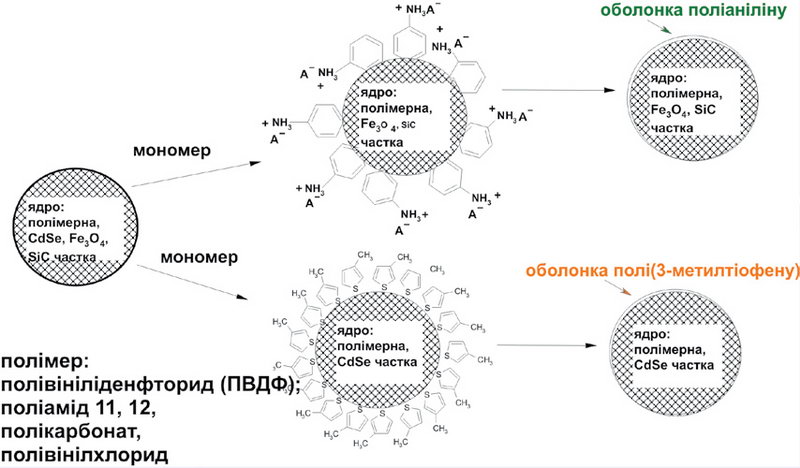
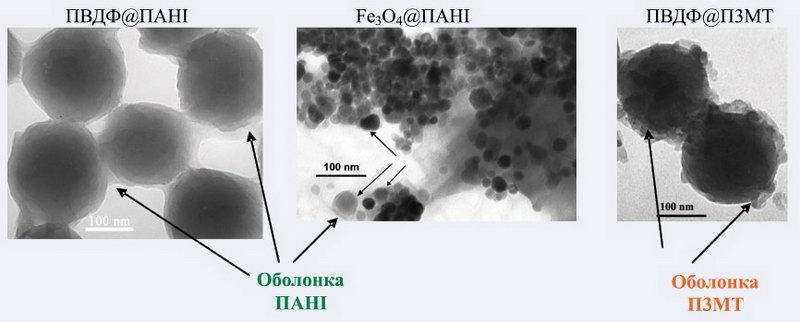
New methods have been developed for synthesizing hybrid semiconductor and magnetic nanomaterials of the polymer or inorganic core-shell type from the semiconductor polymer polyaniline (PANI) or poly(3-methylthiophene) (P3MT). The methods are based on in situ potentiometric control of the polymerization process, which allows tracking its stages and controlling their progress.
Synthesis scheme:
Examples of formed particles of hybrid composites (electron microscope images):
Possible applications of materials: medical diagnostics and treatment; sensor technology, hybrid photovoltaic cells; electromagnetic, antistatic, and anticorrosive protection, etc.
Head of development: Prof. Alexander Arkadyevich Pud, Doctor of Chemical Sciences,
tel.: (044) 559-70-03.
The material is a transparent composite polymer film based on a dielectric industrial polymer (polyethylene terephthalate, polyamide, polycarbonate, polyvinylidene fluoride, etc.), in the surface layer (1-2 μm) of which a polymerization-based sensor polymer, polyaniline (PANI), is distributed. Depending on the chemical state of polyaniline (emeraldine base or salt), the material can interact with substances with acidic properties (vapors or solutions of hydrochloric, acetic, formic acids, etc.) or with basic properties (ammonia, alkali solutions, etc.). As a result of such interactions, PAN changes its color, optical density, and electrical conductivity (Fig. 1), which allows its composites to be used in appropriate sensor devices. The dielectric matrix of the composite ensures high strength and stability of the sensor material.

A sensor system has been developed to register the sensor response of the developed materials in the gas phase based on changes in their optical density (Fig. 2). When using PAN in its basic form, the system gives a linear response to compounds with acidic properties (e.g., formic acid 150-500 ppm), and in its salt form, to compounds with basic properties (e.g., ammonia 4-600 ppm).
The developed material and system can be used in chemical industries where ammonia or various acids are used to detect leaks of these substances into the environment.
Head of development: Alexander Arkadyevich Pud, Doctor of Chemical Sciences, tel.: (044) 559-70-03.

A catalytic adsorption method for desulfurization has been developed, which allows for the effective removal of sulfur-containing compounds, including thiophene, benzothiophene, and their derivatives, from liquid hydrocarbon fuels of petroleum origin.
Unlike known desulfurization methods, the proposed method provides:
During the adsorption-catalytic desulfurization process, sulfur-containing compounds that contaminate petroleum products are catalytically oxidized by available oxidants to polar compounds, which are removed by adsorption. The process can be implemented both in tanks with petroleum products and in a flow-through or flow-through-circulation reactor with a fixed or fluidized bed of adsorbent-catalyst.
Purpose: The technology is designed to improve environmental performance and increase the service life of automotive engines without taking vehicles out of service.
Description of development: The technology consists of periodically restoring worn working surfaces of engine cylinders without dismantling by spraying an anti-wear metal cluster coating through spark plug or injector holes. When engines are treated using this technology, the combustion chamber is cleaned of carbon deposits, the geometry of the cylinders is restored, and scratches on the working surfaces of the cylinders are “healed”, compression is increased by 10-30% and its values are equalized across the cylinders, engine power is increased, and smoke and toxicity of exhaust gases are reduced. With repeated treatment of engines at intervals of 40-50 thousand km of mileage, the service life of engines in the passport mode increases by 2-3 times.
Appearance and results of atomic force microscopy of the coating
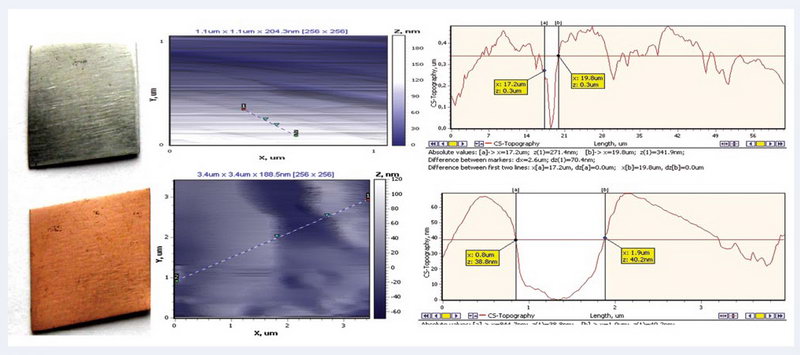
Head of Development: Volodymyr Stepanovych Pylyavskyi, Ph.D., tel. (044) 559-71-81.
Purpose: Solid lubricant coating technology is designed to ensure the operability of parts in dry friction assemblies without the use of liquid or plastic lubricants.
Description of development: The solid lubricating coating (SLC) is produced in the form of a suspension consisting of fluorinated polyamide (PA-24), organic anti-friction filler, and additives (antioxidants, tribopolymerizing components).
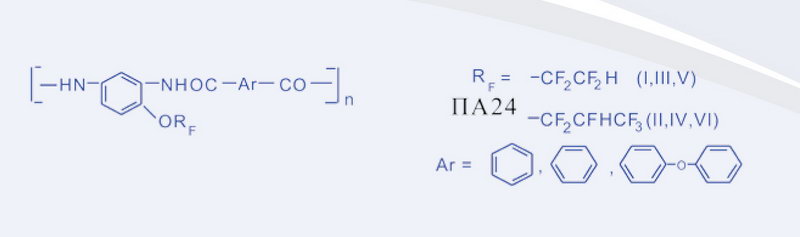
The coating thickness is 0.15 - 0.25 mm.
Heat treatment for hardening is carried out at 190°C for 2 hours, or at 80°C in the presence of a catalyst.

Comparison with analogues: TZP Metal fluoroplastic
The proposed TZP was first used in aviation in the control units of the AN-70 aircraft slats, as well as in robotics on the inner surface of the pneumatic cylinder of a technical robot (the total operation of the pneumatic cylinder was 1,000,000 cycles).
Highly efficient zeolite catalyst and environmentally friendly processes for alkylation of isobutane with butenes to obtain a high-octane gasoline component – alkylate, as well as alkylation of benzene and toluene with C20-C24 olefins to obtain alkylbenzenes for the production of alkyl sulfonate additives for petroleum lubricating oils. The proposed catalyst and developed processes are designed to replace environmentally harmful alkylation processes using highly concentrated sulfuric and hydrofluoric acids and aluminum chloride as catalysts.
The developed catalyst is characterized by increased (by 1-3%) gasoline yields compared to imported samples due to reduced gas and coke formation.
The catalyst is produced from domestic raw materials, mainly kaolin from the Prosyanyivske deposit in the Dnipropetrovsk region, and is planned to be sold at the enamel production facility of the Khimmash Concern (Poltava).
According to the technical and economic feasibility study, capital investments in a plant with a capacity of 10,000 tons of catalyst per year (US$11 million) will pay off within 24-36 months.
The catalyst for reforming light gasoline fractions, which does not contain noble, low-melting, and volatile metals, operates at lower temperatures and pressures than traditional catalysts for this process.
The results of testing the catalyst in the reforming of real gasoline fractions are comparable to the results of reforming on industrial platinum-rhenium catalysts.
Head of development: Lyubov Kazymyrivna Patryliak, Doctor of Chemical Sciences, tel. (044) 559-71-60.

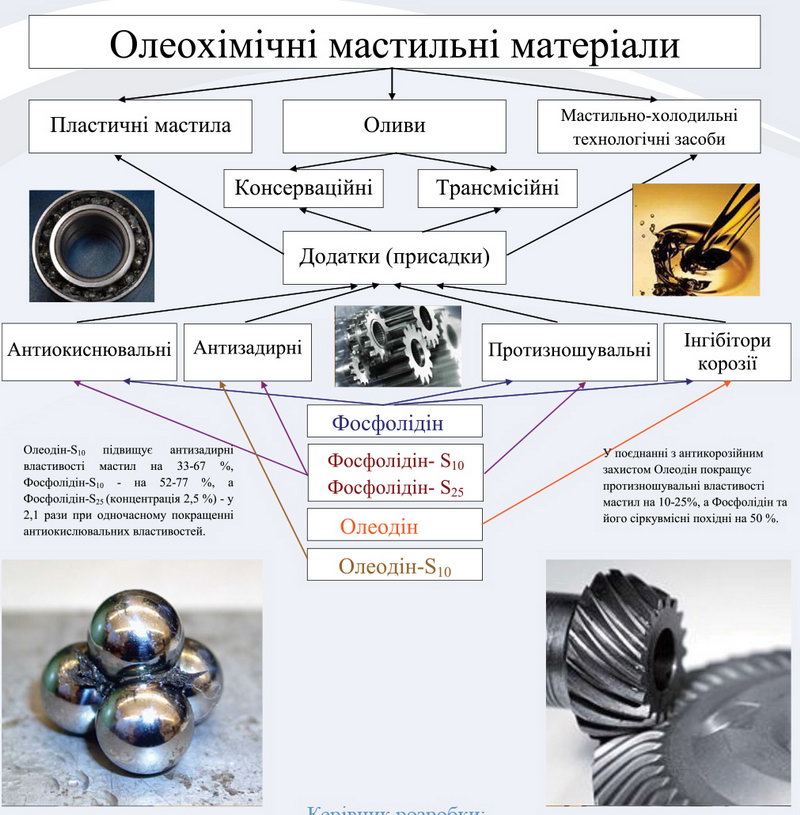
Additive for transmission and industrial oils, plastic lubricants, and lubricating and cooling fluids to improve their tribological and anti-oxidant properties.
Eterol-nS is a series of substances with a sulfur content of n=5–38%; non-volatile, low-hazard brown transparent liquids with a kinematic viscosity at 100°C of 3-8 mm2/s, an acid number of 2-10 mg KOH/g, flash point in an open crucible of 265–270°C and ignition temperature of 319°C; highly soluble in oils.
Improves the viscosity-temperature, protective, anti-seize, and anti-wear characteristics of lubricants under high loads and speeds.
In terms of operational and environmental properties, they are superior to analogues based on fatty acids and their derivatives, and are not inferior to the highly effective analogue “Anglamol” from Lubrizol.

Additive for anti-friction lubricants for rolling or sliding bearings, motor oils, lubricating and cooling fluids, and other friction units of industrial equipment operating under high temperatures, loads, and aggressive environments.
“Phospholidine” is a lubricant-like dark brown substance with a pour point of 27-29°C, easily soluble in hydrocarbons.
It increases the anti-wear properties of lubricants by 50% and their anti-seize properties by 2.1-2.4 times, while improving their toxicological, ecological, and anti-oxidative properties, protective action on cast iron, steel, and copper, and a 2-6-fold reduction in cost compared to the domestic industrial dialkyldithiophosphate additive DF-11.

Anti-friction grease, highly effective in wet and aggressive environments at high temperatures and loads for equipment in the brick, glass, ceramic, and cement industries.
Lubricant-like mass with a dropping point >250°C, yield strength at 20°C – 800-830 Pa, welding load – 7350 N, critical load – 1470-1842 N, improved tribological and protective properties, and increased thermal-oxidative stability. In terms of operational and environmental properties, it outperforms both domestic market products and the best foreign analogue, Ceran HV from Total.

Lubrication of friction parts of metallurgical equipment operating at temperatures ranging from -30°C to +150°C under high loads and possible exposure to aggressive environments.
A grease-like mass with a dropping point >250°C, a strength limit at 20°C of over 400 Pa, increased stability to oxidation at 150°C, and improved protective properties of metal surfaces of friction units against corrosive factors.
In terms of mechanical stability, anti-wear and anti-seize characteristics, the grease outperforms the domestic grease “Uniol-2” and the best foreign analogues.

Specialized grease for friction units with rolling bearings of locomotives, diesel trains, and motor-car rolling stock of railway transport enterprises.
Homogeneous grease-like mass with a dropping point of 190°C, penetration at 25°C within 190-250 m•10-4, viscosity at minus 30°C and an average deformation rate gradient of 10 s-1 – 1650 Pa•s, a strength limit at 50°C of 480 Pa, and a welding load of 2600 N.
Thanks to its improved mechanical stability, low-temperature, tribological, protective, and environmental properties, and performance under high loads in a temperature range from -50°C to +120°C, this grease outperforms both commercial ZRO greases and the best petroleum-based analogues thickened with lithium soaps of fatty acids from expensive castor oil.

V.P. Kukhar Institute
of Bioorganic Chemistry and Petrochemistry
NAS of Ukraine
© 2026 IBOPC NAS of Ukraine